ALOS / Palsar
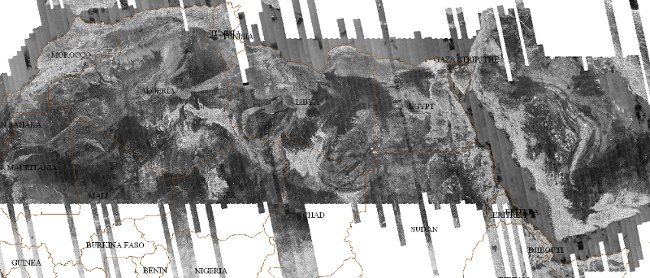
PALSAR mosaic from acquisitions cycles 12 and 13, covering Sahara an Arabia at 50m resolution
In January 2006, the Japanese Space Agency JAXA successfully launched the Advanced Land Observing Satellite (ALOS). It carries two high resolution optical sensors (AVNIR-2 and PRISM) and one full polarimetric L-band SAR, named PALSAR. This phased array SAR provides high resolution (10 m) imagery at variable incidence angles, with a geolocation accuracy better than 10 m and the radiometric accuracy better than 1 dB. The PALSAR instrument is operated to provide systematic wall-to-wall observations of all land areas on the Earth on a repetitive basis.
A full coverage of the Sahara in HH and HV polarizations was acquired in June and July 2007, during ascending cycles 12 and 13. The 10 m full-resolution data were processed by JAXA to 50 m strip products, which were ingested into our data processing and mosaicking software. We developed a fully automated data processing chain that produces geocoded 1° x 1° SAR scenes that can be then superposed to the corresponding SRTM squares. More than 400 dual-polarization PALSAR strips were needed in order to cover the entire Sahara and Arabia. The final mosaic covers latitudes between 17-37°N and longitudes between 17°W and 60°E. Geocoded 1° x 1° PALSAR squares are managed with the help of a web map server (MapServer), that allows to import and display PALSAR data under Google Earth. This allows a very simple and convenient access to the radar data, and makes comparison between optical and radar data easy.
This PALSAR data set constitutes a unique tool for the scientific community to study the paleo-environment and paleo-climate of North Africa. It will also help building more complete geological maps, in support to future water prospecting.
Ph. Paillou, S. Lopez, T. Farr, A. Rosenqvist, "Mapping Subsurface Geology in Sahara using L-band SAR: First Results from the ALOS/PALSAR Imaging Radar", IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, vol. 3, no 4, pp. 632-636, 2010.